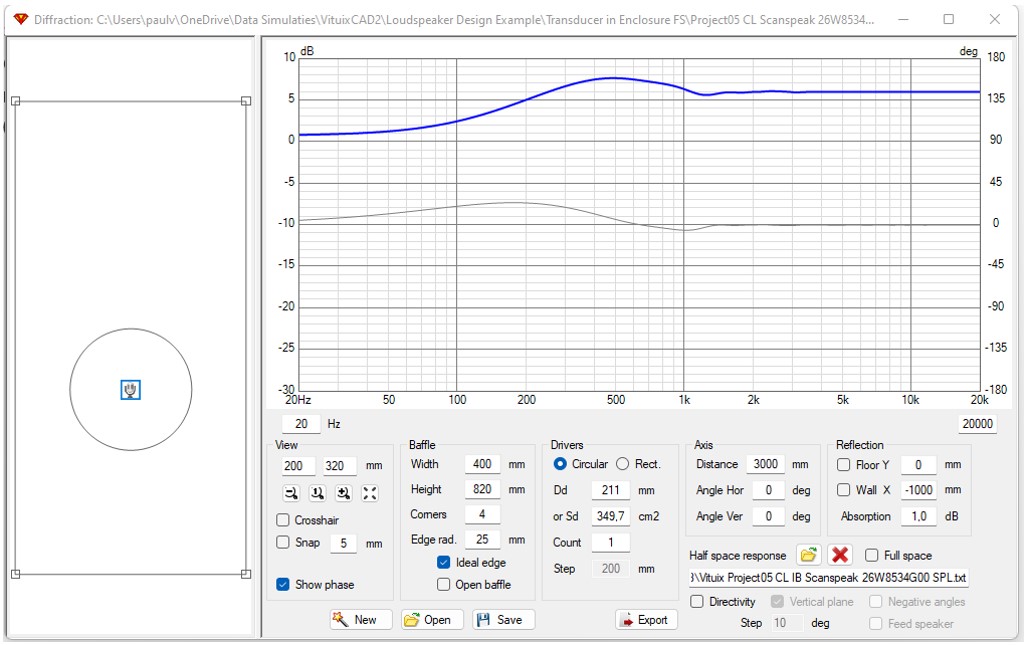
Transducer in enclosure in full space
The transducer is placed in an enclosure and the cabinet is placed in a full space domain. In this domain there are no boundaries surrounding the enclosure. Radiation is produced into a full space (4π) field in all directions. There are no reflections from any direction. Since all sides of the enclosure are within the radiation field, diffraction takes place around the entire shell of the enclosure.
At low frequencies there is a substantial reduction of the SPL response compared with the SPL in enclosure on infinite baffle. The low frequency radiation is spreading out around the box into twice the available space and the SPL becomes 6 dB lower.
At medium frequencies the directivity of the enclosure itself begins to act as a baffle, causing the response to approach the same and even higher levels as seen in the infinite baffle response.
At high frequencies the transducer itself becomes directional and the SPL is equal to the infinite baffle SPL response.
Contents
- Simulation of the SPL in the full space domain
- Comparison SPL of the transducer in enclosure on infinite baffle and in full space – baffle step ratio
Simulation of the SPL in the full space domain
The full space response can be simulated with a CAD tool using the “SPL response in enclosure on infinite baffle” for the transducer.
The VituixCAD diffraction tool can be used to simulate the SPL response in full space.
As example the Scanspeak woofer 26W8534G00 is used, mounted on a front baffle as it is been used for the VCL EM2 loudspeaker.
Start (VituixCAD->Tools->SPL Diffraction)
Baffle, driver model and position
for the baffle:
- set width to “400 mm”
- set height to “820 mm”
- set corners to “4”
- set ideal edge “on” and open baffle “off”
for the woofer transducer:
- set diameter to “211 mm”
- set count to “1”
for the axis:
- set Distance to “3000 mm” (mean listening distance)
- set Angle Hor and Angle Ver to “0” ( on axis response)
for reflection: set all off (full space)
Push the “New” button below on the window. The baffle and transducer appear in the left window. Position of the transducer and the microphone icon can be adapted by selecting them by the mouse and drag to the right position. The position can be read out in the View window.
For the loudspeaker example the coordinates of the woofer transducer are 200 mm horizontal and 320 mm vertical. The coordinates of the microphone are also 200 mm horizontal and 320 mm vertical.
SPL response of the transducer in enclosure in full space
Open the SPL response of the transducer in enclosure on infinite baffle with the ‘Half Space Response’ button.
Set Full Space to “on”.
Set Directivity to “off”.
Directivity will be investigated later in the off axis, power and directivity analysis.
Now the SPL response of the transducer in enclosure in full space is shown in the output window.
With the Export button the full space SPL response can be saved as a text file.
The domain space has no influence on the impedance. The impedance is the same as the impedance of the transducer in enclosure on infinite baffle.
With the Save button the baffle project is saved as a “vxb” file.
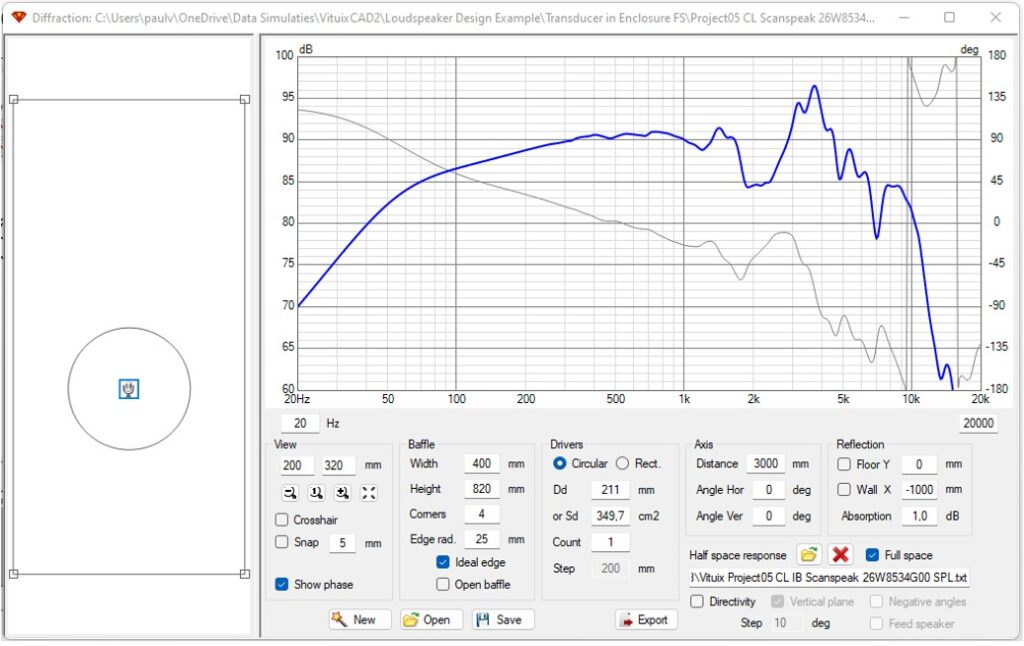
Comparison SPL of the transducer in enclosure on infinite baffle and in full space – baffle step ratio
Start (VituixCAD->Tools->SPL Enclosure)
The Enclosure project of the Scanspeak 26W8534G00 like described in the Technical Page 08 Transducer in enclosure on infinite baffle can be used.
While cursor on SPL chart in Enclosure window, select “Open overlay…” with mouse right click.
Select both the SPL of the transducer in enclosure on infinite baffle and in full space for the Scanspeak 26W8534G00.
While cursor on SPL chart in Enclosure window, select “traces” with mouse right click. Only select the two imported SPL responses.
The following SPL chart is displayed in the Enclosure window.
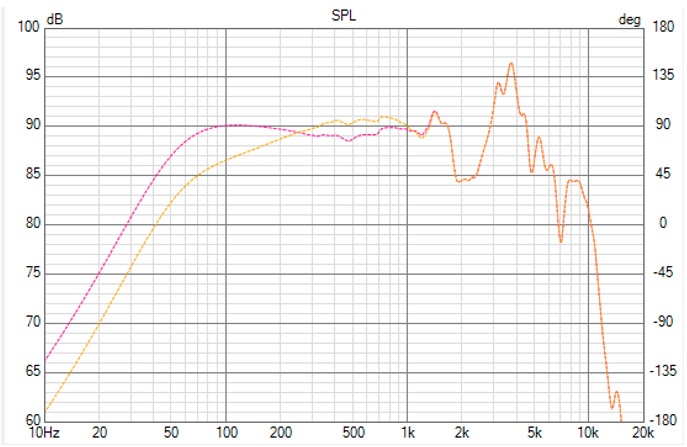
This is an interesting chart to analyze.
The SPL of the transducer in enclosure on infinite baffle is displayed in pink color.
The SPL of the transducer in enclosure in full space is displayed in orange color.
Like expected, the impact of the different domains infinite baffle and full space can be observed.
At low frequencies there is a reduction in the full space response, up to -6 dB. At high frequencies, no changes between the full space and infinite baffle domains. At medium frequencies, there is a rise or bump in the full space response. This is where the directivity of the enclosure itself begins to act as a baffle, causing the full space response becomes even higher than the infinite baffle response. This rise is determined by the cabinet shape and the position of the transducer on the baffle.
The ratio of the full space response over the infinite baffle response is called the baffle step response of a transducer mounted in an enclosure and placed in a full space domain.
The baffle step ratio can be made visible also in the Vituix Diffraction tool.
Open again the “vxb” baffle project of the Scanspeak 26W8534G00.
In the output menu below, set Full space to “off”. Now the baffle step response is displayed in the output window.
With the export button, this ratio response can be saved as a text file.